Liver Transplant
Live A Healthy Life
Liver Transplant
Dr L H Hiranandani Hospital
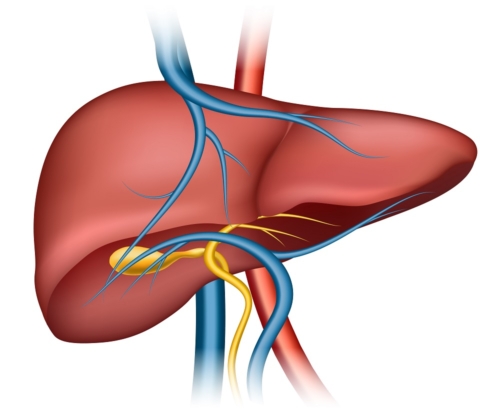
Liver is the largest abdominal organ. Liver weighs about 1200 – 1500 grams in an average roughly 2% of body weight. Liver, though a single organ, broadly it can be divided into two parts – right and left liver and 8 independent segments (each having its own blood supply and biliary drainage) functioning as a single organ. Liver as a whole has a hepatic artery supplying oxygenated blood, a portal vein carrying blood from intestines to liver and bile ducts draining bile formed in the liver to intestines. Blood from liver is delivered to heart via three hepatic veins.
Liver produces bile which is drained by biliary tree. Gall bladder is a reservoir for the bile lies on the liver bed, and is attached to bile duct. It regulates delivery of bile into intestines. Liver is endowed with remarkable capacity to regenerate after division into parts. This is the basis of Live Related Liver Transplants, and the reason why live related liver transplant is possible.
Who Requires A Liver Transplant?
Liver failure causes many problems, including malnutrition, problems with blood clotting, bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract, and jaundice. Frequently, patients who undergo liver transplantation are quite ill, and require hospitalization in the Intensive Care Unit prior to surgery. A large, upper abdominal specialized incision is used for liver transplant.
Liver transplants are performed in many centers across the country. The healthy liver is obtained either from a living donor or from a donor who has recently died but has not suffered liver injury. The diseased liver is removed through an incision made in the upper abdomen. The new liver is put in place and attached to the patient’s blood vessels and bile ducts. The operation can take up to 12 hours to complete and may require large volumes of blood transfusions.
Patients require hospital care for one to four weeks after liver transplant, depending on the degree of illness. After liver transplantation, patients must take immunosuppressive medications for the rest of their lives to prevent immune rejection of the transplanted organ
Liver transplant may be necessary for patients who suffer from:
- liver damage due to alcoholism (Alcoholic cirrhosis)
- primary biliary cirrhosis
- long-term (chronic) active infection (hepatitis B or C)
- liver (hepatic) vein clot (thrombosis)
- birth defects of the liver or bile ducts (biliary atresia)
- metabolic disorders associated with liver failure (e.g., Wilson’s disease)
What are the types of Liver Transplants?
Deceased Donor (Cadaver) – Liver is obtained from patients who are brain dead. (They are actually dead for from legal, ethical, spiritual and clinical point of view). Once a brain dead patient is identified, and is deemed as a potential donor, the blood supply to his body is maintained artificially. This is the principle of deceased organ donation. Young patients who die of accidents, brain hemorrhage or other causes of sudden death are the donors suitable for organ donation.
Living Donor – Part of liver from living related donor is a certain and timely available option and only hope for cure. Liver surgery can be carried out safely in almost all patients. All patients are listed for deceased donor liver but timely organ availability is uncertain. Liver has the capacity to regenerate if a part of normal healthy liver is removed. Hence we can divide part of liver from a live donor and implant it into another patient. In a live donor liver transplant, a portion of the liver is surgically removed from a live donor and transplanted into a recipient immediately after the recipient’s liver has been entirely removed.
Donor safety is the first objective of whole process. Utmost care is taken while selecting and operating liver donors. The risk of serious morbidities following a living donor liver resection is 10%.The risk of death in the donor is 0.02to 0.05%. Live donor liver transplantation is possible because the liver (unlike any other organ in the body) has the ability to grow back to its original size. The regeneration of liver following surgery is complete by 4 to 8 weeks.
Some Facts About Liver Transplants?
- A liver transplant is needed when the liver fails, usually because of long term disease.
- About 1,00,000 people in India die of liver failure every year.
- First successful liver transplant was done in 1967
- The number of liver transplants has been steadily increasing for more than 15 years.
- Cirrhosis is the most common reason for liver transplant
- Donated livers can come from either diseased donors or living donors.
- The five year survival rate of liver transplant patients is over 70%.
About Our Liver Transplant Doctors In Mumbai

Dr. Swapnil Sharma
Full-Time Consultant – Liver Transplant, HPB, and GI Surgeon
Qualifications
M.B.B.S., MS, DNB (GI Surgery), Fellowship in Liver Transplant & HPB Surgery
What Our Patients Says About Us
Don’t Take Our Word. See What Our Patients Said About Us.
India
Kenya
United Kingdom
Locate Us
Address
Hill Side Avenue, Hiranandani Gardens,
Powai, Mumbai – 400 076.
